Programme of the ESB Engineering diploma in wood and biosourced materials science and technology
5 years of HE
The engineering programme uses both teaching periods devoted to a subject (theme) and hands-on periods.
The programme includes modules in French and in English. The International Timber Trade’s speciality is fully taught in English.
Allowing you to customise your study path is a key feature of the curriculum. During your studies, you can choose from a range of courses and study contexts to help you develop your career plans:
Work Experience periods in companies enable students to acquire skills linked to their academic training.
They take the form of work placements for students and in-company assignments for apprentices.
In the 1st year, the in-company period gives you an insight into the industrial environment and the formalisation of a problem. You observe a workstation and suggest improvements.
In Year 2, you carry out an industrial improvement study of a process, product or service. During this in-company assignment, you will be tested on your ability to correctly pose a problem and propose solutions based on methodological work.
You will complete an independent engineering assignment. All aspects of the course are brought into play to respond to an industrial problem: science, technology, economics, management, innovation, etc. This assignment is the subject of an end-of-studies professional report, which is presented to a jury.
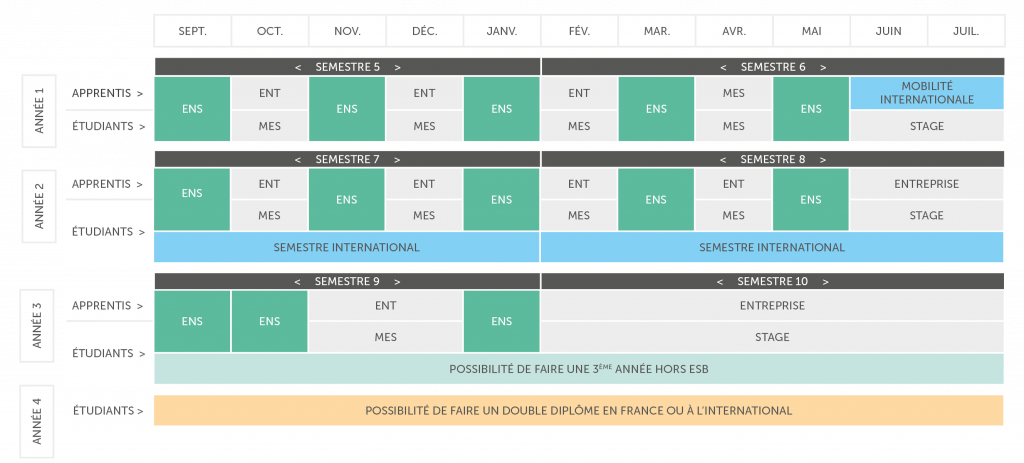
Firts semester – Designed to give students the knowledge and know-how required throughout the training programme: project management, familiarity with materials, circular economy basics, fundamental sciences, communications, etc.
Second semester – Prepares students for initial orientation choices. During this semester, students learn about the various specialities and digital tools. They carry out an initial circular economy project.
SEMESTER 5
The basics
Wood and biosourced materials
Circular economy 1 – supply and resources
Project 1 – Scientific project (3 ECTS)
Human and social sciences (2 ECTS) : inter-cultural opening, office software applications, introduction to neuroscience, communication and involvement
Foreign languages
SEMESTER 6
Circular economy 1 – generalities
Professional project
Engineering and digital technology
Projects 2 : scientific, technological, or innovative project (3 ECTS)
Human and social sciences (2 ECTS)
Foreign languages
Professional experience in a company (7 ECTS)
During these year, students develop their first minor to be chosen from 6 available specialities. Students also need to choose elective courses that will allow them to develop in-depth knowledge of wood science, engineering science, digital technology, production automation, etc.
Foreign exchange programmes are available during semesters 7 or 8 in the second year. ESB offers nearly 37 destinations including 4 dual degrees (Switzerland, Brazil, Chile, and Canada).
SEMESTER 7
Circular economy 2 – Eco conception
Circular economy 3 – Strategy and sustainable management
Elective courses (for a total of 8 ECTS):
Project 3 (3 ECTS) :
Human and social sciences (3 ECTS)
Foreign languages
SEMESTER 8
Circular economy 3 – Strategy and sustainable management
Elective courses (for a total of 12 ECTS):
Project 4 (3 ECTS) :
Human and social sciences (1 ECTS)
Foreign languages
Professional experience in a company (8 ECTS)
The 1st semester is totally dedicated to the professional project. Students choose a second minor and a major related to one or the other of the minors followed.
The second semester takes place entirely in a company, where the student carries out an end-of-study project.
SEMESTER 9
Minor 2 (4 ECTS)
Major (22 ECTS)
Human and social sciences (1 ECTS)
English (3 ECTS)
SEMESTER 10
Business game (2 ECTS)
End of studies project (28 ECTS) carried out as part of a work-study program or an 20-week traineeship.
In the 2nd and 3rd year, the students choose the lessons necessary for their professional project grouped into minors and majors.
This speciality is aimed at students who wish to practice a profession at the forest/industry interface. Engineers who graduate from this programme are able to harvest forest products using a sustainable approach and make efficient use of this resource.
UE for the Efficient use of forest production minor (A1)
UE for the Efficient use of forest production major (A1)
The engineers who choose this speciality are capable of managing the production of wood products and participating in their design. These engineers contribute to logistics and product development.
UE for the Production and processes minor (A2)
UE for the Production and processes major (A2)
This speciality prepares engineers for international trade and negotiation and ensures they are capable of reformulating the client’s need and coming up with relevant solutions. They identify new markets in the international context and help the company’s offer to progress.
UE for the International timber trade minor (A3)
UE for the International timber trade major (A31)
Engineers specialised in wood construction manage construction projects that use wood and/or biosourced materials. They are capable of integrating constructive solutions that use wood and wood-derived products in building.
UE for the Wood construction minor (A4)
UE for the low-carbon construction and housing – design office major (A41)
UE for the low-carbon construction and housing – project management major (A41)
Engineers who choose this speciality are trained to understand the corporate innovation process and implement innovative solutions in various processes: supply and procurement, production, marketing, distribution.
UE for the Innovation minor (A6)
UE for the Innovation major (A61)
R&D engineers develop new materials or processes including wood or wood-derived materials. They manage research projects from the initial study phase through to the industrial application of the product.
UE for the Research minor (A5)
UE for the Research major (A51)
Engineering students (excluding apprentices) can complete their 3rd year in another institution in France or abroad.